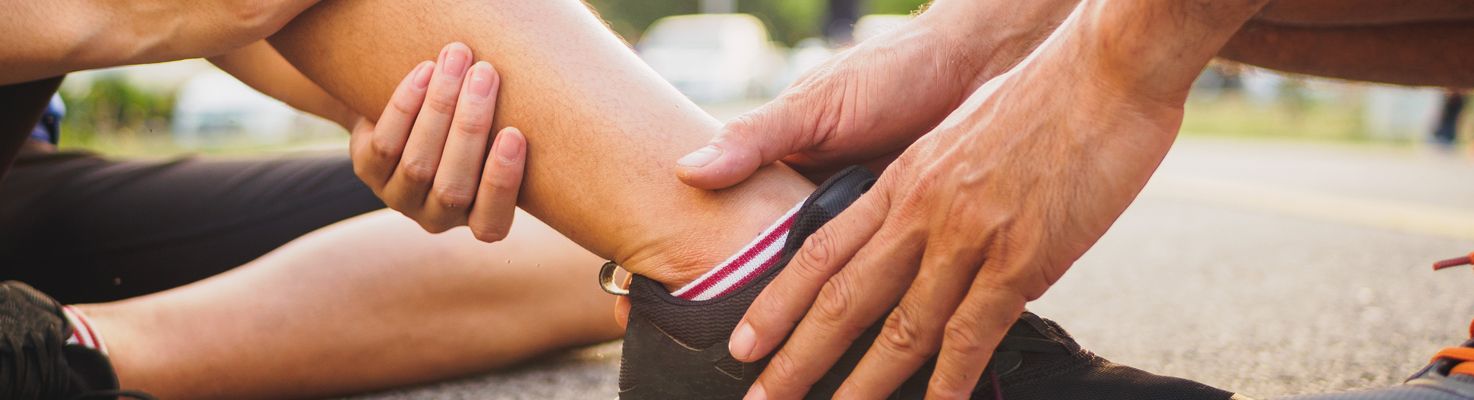
Sports injuries refer to any musculoskeletal injury sustained during physical activity or participation in sports due to overuse or trauma. Common sports injuries include sprains, ACL tears, fractures, rotator cuff tears, tennis elbow, and dislocated joints. These injuries can affect various areas of the body, including the shoulder, elbow, knee, foot, ankle, neck, and back.
By Arete Orthopaedic Centre
Medically Reviewed by Dr Wang Lushun
Both seasoned athletes and common people alike can be affected by sports injuries. Sports injuries can manifest in
various forms, ranging from minor sprains and strains to severe fractures and tears. These injuries can occur
suddenly due to a trauma or accident (acute) or develop over time due to excessive use (chronic). Some common sports
injuries include:
A sprain is an injury to a ligament that occurs when a joint is forced into an unnatural position, causing the
ligament to stretch or tear. On the other hand, a strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon often caused by
overstretching, twisting, or pulling of the muscles. These injuries affect the ankles, knees, and wrists.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
A sprain or strain may have the following symptoms:
- Pain and swelling in the injured area
- Bruising or discoloration
- Limited range of motion
Treatment
Treatment options for sprains and strains can range from conservative methods to surgical procedures.
- RICE Method: This method involves resting the injured area, applying ice, compressing the injury, and elevating the injury area above heart level to reduce swelling.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy involves a combination of exercises and manual therapy techniques to restore strength, flexibility, and overall function.
- Bracing Supports: Splints or crutches provide additional support to the injured area to reduce strain and facilitate recovery.
- Pain-relief Medications: For pain relief, over-the-counter medications can alleviate the discomfort and inflammation associated with sprains and strains.
- Surgery: Most cases of sprains and strains can be managed without surgery. However, in some serious cases, it may be needed, such as a complete tear of a ligament, muscle, or tendon; or a significantly unstable joint due to a severe sprain.
ACL Tears
An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear refers to the rupture of a strong band of tissue that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia) and provides stability to the knee joints. This injury is caused by sudden twisting or pivoting motions while the foot remains firmly planted on the ground. Most ACL tears occur in sports involving sudden stops or changes in direction, such as soccer, basketball, football, and skiing.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
An ACL tear is typically accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A popping sensation in the knee
- Immediate pain and swelling
- Instability in the knee
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected leg
Treatment
Treatment for ACL tears varies depending on its severity. An orthopaedic surgeon may recommend:
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist will provide exercise programmes to strengthen the surrounding muscles, improve the range of motion, and restore stability to the knee.
- ACL reconstruction: This is performed when the ACL has been completely torn or when the knee is severely unstable. During surgery, a graft from the patient's own tissue (autograft) or a donor (allograft) is used to replace the torn ACL.
Rotator Cuff Tears
This refers to an injury that affects the rotator cuff, a network of muscles and tendons that hold the upper arm
bone (humerus) in place within the shoulder joint. Rotator cuff tears can occur due to a sudden fall or accident
(acute tear) or the gradual wearing down of tendon tissues with age (degenerative tear). They also frequently occur
in athletes who engage in overhead arm movements, such as tennis, weightlifting, and baseball, as well as workers
who perform routine tasks such as wall painting.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
The common symptoms of a rotator cuff injury include:
- A dull ache when lying on the affected shoulder or when lifting and lowering the arms
- Weakness in the arm, accompanied by pain and stiffness
- A crackling sensation when moving the shoulder in certain positions
Treatment
Rotator cuff injuries can be treated in several ways, including:
- Strengthening Exercises: This involves customised exercise programs designed for muscle strengthening around the shoulder joint and improving its flexibility.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroid injections can be prescribed to reduce the pain and inflammation caused by rotator cuff tears.
- Open Rotator Cuff Repair Surgery: For severe cases, this procedure involves making a long incision to access the torn tendon and reattach it to the bone using sutures.
- Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure uses small incisions and a specialised instrument with a fibre-optic camera (arthroscope) to repair the rotator cuff.
Fractures
A fracture occurs when a fall, or a high-impact blow or collision causes damage to the bones. This injury can be
severe enough to puncture through the skin (open fracture) or may be less severe and is not visible through the skin
(closed fracture). Most fractures happen in the arms, hands, and fingers, especially among athletes and those who
frequently place strain and stress on their bones.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
Patients with bone fractures typically experience the following symptoms:
- Sudden pain, swelling, and bruising in the affected area
- Inability to move or use the injured area or nearby joints
- Discolouration of the skin around the affected area
- Deformity and inability to bear weight
Treatment
Orthopaedic surgeons utilise various approaches to treat bone fractures depending on their severity:
- Immobilisation: This involves the use of splints, casts, or braces to restrict movement and keep the fractured bone stable while it heals.
- Closed Reduction: In this procedure, the doctor manually aligns the broken bone back into its normal position without the need for surgery. The patient is normally given anaesthesia or sedation to ensure comfort; and once done, the affected area will be immobilised with splints or casts to restrict movement while the bones heal.
- Bone Fracture Surgery: A surgeon will realign the fractured bones and use internal fixation devices such as plates, screws, rods, or pins to hold the realigned bone in place. This treatment is recommended for severely displaced bones or open fractures.
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, is a condition characterised by pain and inflammation in the
tendons that connect the forearm muscles to the outer part of the elbow. This typically affects individuals who
perform repetitive activities which place stress on their forearms, wrists, or hands, including tennis players,
golfers, and baseball players, as well as assembly line workers and painters.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
Some common symptoms of tennis elbow are as follows:
- Pain and tenderness around the elbow and forearm
- Pain that extends down the wrist, even during rest
- Difficulty with tasks that require arm bending or straightening
- A decrease in grip strength
Treatment
Tennis elbow can be managed with various treatments, such as:
- Counterforce Braces or Bands: These supportive devices are worn around the forearm, just below the elbow, to relieve pressure on the affected tendon.
- Steroid or Plasma Injection: A doctor may administer either a corticosteroid or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection directly into the affected area to help minimise soreness and stiffness.
- Shockwave Therapy: This procedure utilises acoustic energy to stimulate blood flow and promote tissue regeneration in the affected area.
- Open Surgery (Tennis Elbow Release): During this procedure, the surgeon will make an incision above the bone on the side of the elbow to remove damaged tissue while releasing tension on the affected tendon.
- Arthroscopy: This procedure involves making small puncture holes on the side of the elbow joint and inserting an arthroscope and specialised surgical tools to visualise and repair the affected tendon.
Dislocation
Dislocation is an injury in which bones connected through a joint are displaced from their normal positions,
following a sudden impact on the joint. This condition often occurs in contact sports such as basketball and
football. It may affect various joints throughout the body, including the shoulder, hips, and knees.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
A person with a dislocated joint may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain during movement
- Swelling, bruising, or numbness in the affected area
- Visible deformity
- Joint instability or weakness
Treatment
Managing dislocations normally involves the following:
- Manipulation or Repositioning: The doctor manually adjusts the dislocated joint to its correct position. This typically involves anaesthesia or sedation to reduce pain and muscle tension.
- Immobilisation: Stabilising the joints using splints, casts, or other assistive devices is crucial to promote healing and prevent further damage during the recovery period.
- Medications: Pain medications may be given to manage symptoms of pain and swelling.
- Surgery: In severe cases, a doctor will make a surgical incision to access the dislocated joint before manually manipulating the joint back to its normal position. If there is damage to any soft tissue, or a fracture, surgical repair may also be performed then.
Shin Splints
Shin splints, also called medial tibial stress syndrome, is a condition characterised by pain along the shinbone
(tibia). It typically arises during physical activities that involve repetitive strain on the lower legs, such as
running or jumping. Shin splints often result from overuse or excessive impact on the muscles, tendons, and bone
tissue.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
Common symptoms of shin splints include:
- Dull, aching pain along the inner side of the shinbone
- Gradual onset of pain
- Soreness and tenderness
- Mild swelling
- Possible stiffness of the lower leg
Treatment
Shin splints can typically be resolved through conservative treatments. However, surgery may be required in severe cases where conservative treatments have failed, and there are signs of other underlying structural issues. Treatment options for shin splints include:
- Medications: Certain medications can ease both pain and swelling associated with shin splints.
- Compression Techniques: This involves using elastic compression bandages or sleeves to support the lower legs and prevent further inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: To relieve pain associated with shin splints, a physiotherapist may recommend stretching and strengthening exercises targeted at the lower leg muscles.
- Orthotics: In some cases, shin splints may result from overpronation or flat feet. Custom orthotic inserts or shoe modifications may be recommended to correct biomechanical abnormalities.
- Surgery (Fasciotomy) - This procedure is performed to treat severe shin splints caused by compartment syndrome. It involves releasing the connective tissue (fascia) surrounding the affected compartment to relieve pressure and alleviate symptoms.
Achilles Tendon Tear
This condition occurs when the Achilles tendon, a large tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone, is completely or partially ruptured as a result of sudden movements that exert force on the tendon.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
A ruptured Achilles tendon may exhibit symptoms such as:
- Sharp pain in the back of the ankle near the heel
- Swelling and bruising in the affected area
- Pain while walking
- Tenderness at the site of the tendon tear
- A popping or cracking sensation that occurs during an injury
Treatment
Initial treatment for the Achilles tendon involves the RICE method to reduce swelling and discomfort. This is often complemented with medical treatments to facilitate healing, such as:
- Brace or Walking Cast: A brace or cast is used to immobilise the foot and ankle. These supportive devices may need to be worn for several weeks or months.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy includes exercises to improve the strength of the Achilles tendon and leg muscles to facilitate recovery.
- Surgery: Surgery for a ruptured Achilles tendon involves creating an opening in the posterior region of the lower leg and reattaching the torn tendon. The surgeon may also remove the deteriorated tendons and stitch together the remaining parts.
Cartilage Tear
This refers to an injury or damage to the cartilage, which is a tough, flexible connective tissue that acts as a
cushion to reduce friction between bones and allow for smooth joint movement. Cartilage tears can be caused by
sudden, forceful impact or degenerative changes.
Symptoms & Treatment
![]()
![]()
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with cartilage tears include:
- Stiffness or swelling around the knee joint
- Difficulty bearing weight
- A popping or buckling sensation
- Difficulty in fully straightening the knee
Treatment
Non-surgical treatments for cartilage tears include the RICE method, anti-inflammatory medications, using crutches, and physiotherapy. In severe cases, surgery may be needed:
- Debridement: This procedure involves smoothing the damaged cartilage and removing loose edges to reduce friction and prevent potential irritation.
- Arthroscopic Microfracture: The surgeon makes tiny holes, or microfractures, in the damaged cartilage to expose the blood vessels within the bone. This causes a blood clot to form inside the cartilage, stimulating the growth of new cartilage tissue.
- Autologous Cartilage Implantation: Here, the surgeon harvests healthy cartilage cells from the patient's knee. These cells are then cultured in a laboratory before being implanted back into the joint, where they develop into new cartilage tissue.